Electrodialysis (EDI) is a technology that uses electric field force to drive the movement of charged particles (ions) in a solution through ion exchange membranes to achieve the purpose of separating, desalinating, and concentrating specific ions in the solution. It is widely used in fields such as water treatment, chemical industry, food processing, and environmental protection.
Working principle:
The electrodialysis system usually consists of the following parts:
Ion exchange membrane: Electrodialysis uses selectively permeable ion exchange membranes, usually including cation exchange membranes (allowing cations to pass through) and anion exchange membranes (allowing anions to pass through). These membranes are arranged alternately in an electrodialysis stack.
Electrodes: Electrodes, namely anode and cathode, are set at both ends of the electrodialysis stack. A direct current voltage is applied to the electrodes to form an electric field.
Compartment: The ion exchange membrane divides the electrodialyzer into multiple compartments. Each compartment is separated by a membrane to form a concentrated compartment and a dilute compartment.
When a direct current voltage is applied to the electrodes, the cations (positive ions) in the solution will move towards the cathode, while the anions (negative ions) will move towards the anode. Due to the selective permeability of the ion exchange membrane, ions can only move along specific paths:
Cations can only pass through cation exchange membranes and move from the concentrated compartment to the dilute compartment.
Anions can only pass through anion exchange membranes and move from the concentrated compartment to the dilute compartment.
In this way, the ion concentration in the concentrated compartment gradually decreases, while the ion concentration in the dilute compartment gradually increases, realizing the desalination or concentration of the solution.
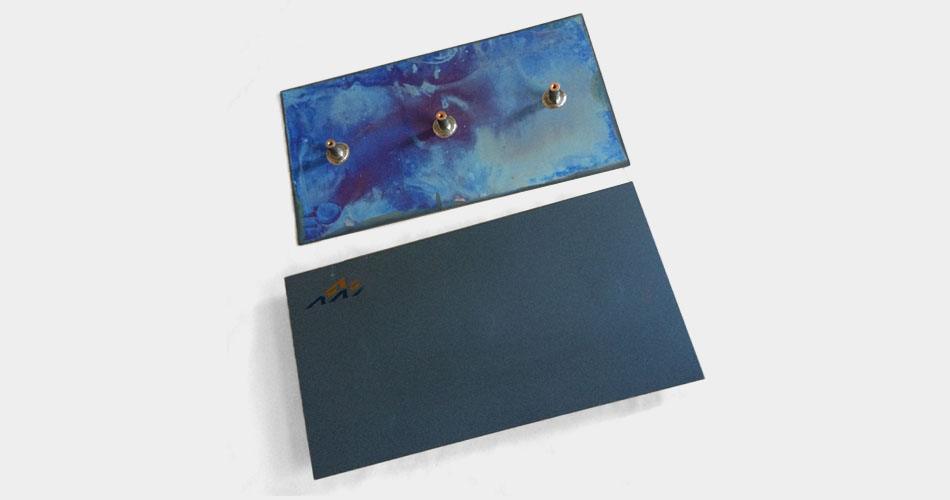
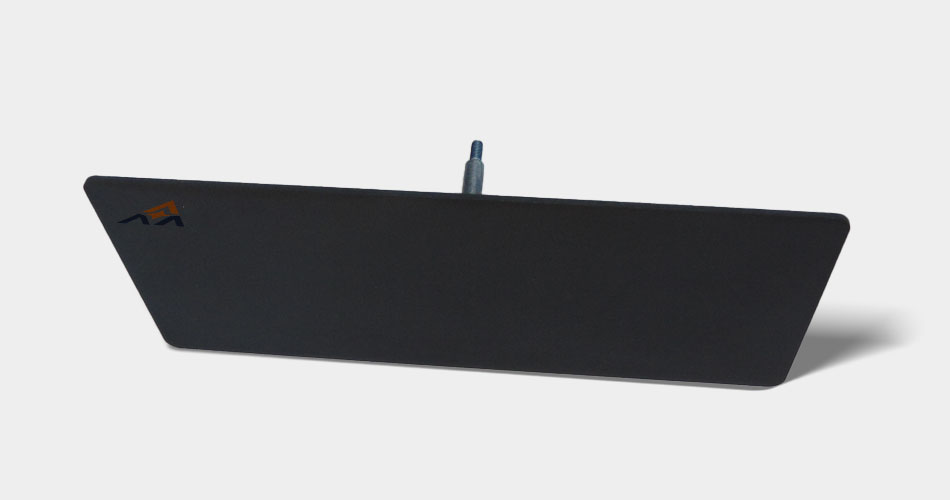
Titanium anode for electrodialysis is an important part of electrodialysis technology.
The titanium anode plate for electrodialysis has excellent corrosion resistance and good electrical conductivity, and is very suitable for use in an environment involving electrolyte solutions such as electrodialysis. In the electrodialysis process, the titanium anode plate for electrodialysis, as part of the electrode, provides an electric field for the migration of ions.
Since electrodialysis is usually used in fields such as water treatment, chemical industry, food processing and environmental protection, the solutions in these fields may be highly corrosive, while the titanium anode plate can maintain stable performance under harsh conditions.
The quality and performance of the titanium anode plate for electrodialysis play a key role in the efficiency and reliability of the electrodialysis system. High-quality titanium anode plates should have a uniform coating, good electrical conductivity and a long service life to ensure the stable operation of the electrodialysis process and the efficient separation, desalination or concentration of specific ions in the solution.
With the continuous progress of technology, our research and development of titanium anode plates for electrodialysis is also deepening continuously to meet the needs of different application scenarios and improve the overall performance and application range of electrodialysis technology.
Common Coating Types and Their Applications
Applications of Titanium Anodes in Electrodialysis
1.Desalination and Water Softening
Seawater and Brackish Water Desalination:
RuO₂-IrO₂/titanium anodes in ED reverse osmosis (EDRO) systems achieve >99% salt removal from seawater, producing potable water with <500 mg/L TDS.
Example: A Mediterranean desalination plant using these anodes treated 10,000 m³/day of seawater with energy consumption <3 kWh/m³.
Industrial Water Softening:
Removes Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺ from cooling tower water, preventing scale formation. Titanium anodes maintain stable performance in high-hardness water (e.g., 1,000 mg/L CaCO₃).
2.Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Metal Plating Rinses:
Recovers valuable metals (Ni²⁺, Cu²⁺) from electroplating wastewater while purifying rinse water for reuse. SnO₂-Sb₂O₃/titanium anodes enable >95% metal ion removal.
Food and Beverage Processing:
Removes salts and organic acids from cheese whey or juice concentrates, improving product quality and enabling water recycling.
3.Chemical Recovery and Purity Enhancement
Acid/Base Separation:
Separates sulfuric acid from metal sulfate solutions in hydrometallurgy using ED with PbO₂/titanium anodes, achieving >90% acid recovery.
Pharmaceutical Purification:
Removes ionic impurities from drug solutions, supporting GMP-compliant production. BDD/titanium anodes ensure no metal leaching into sensitive pharmaceutical formulations.

Who we are ?
Qixin titanium Co.Ltd, is a leading manufacturer specializing in coated titanium anode. With an extensive historyand a wealth of expertise, we have been dedicated to providing high-quality products and solutions to variousindustries for many years.Our company was established 2006, and since then, we have accumulated 18 years of valuable manufacturingexperience. This experience has enabled us to master the art and science of producing top-notch coated titaniumanodes that meet the most stringent quality standards.We take pride in our state-of-the -art manufacturing facilities and a team of highly skilled professionals. Ourengineers and technicians are experts in the field, constantly researching and innovating to improve our productsand processes.
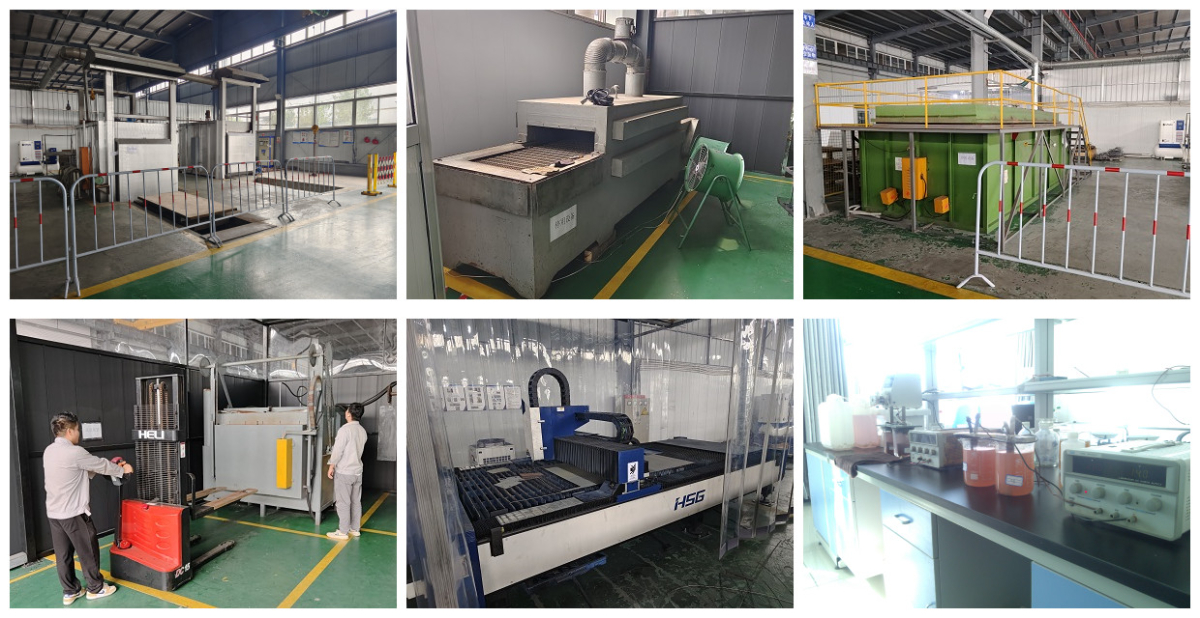

production
1. Substrate treatment: it needs to be treated by roughing, cleaning and removing oil, which can increase the compactness of catalytic.
2. Brushing coating:After substrate treatment, it will be proceeded brush coated. The main coated content is platinum group metal, which is a kind of mixed solution.Then, heat treatment will be going on after drying.The whole procedure need to be repeated many times. This method is better to form thin oxide catalytic that is lamellar adhere to substrate surface.

Quality assurance and after-sales service
1. We promise that our substrate is high quality,acceleratd life test.The coating solution is configured according to the certain proportion.
2. With the high technology and equipment,All of our tecnical personnel have abundant experience,and our workers are very skilled.During the production of the Titanium anode, each process must carry on the strict examination,Such as the detection of surface rougghness,The quality of coating solution,coating evenness and so on.
3. We have our own production,sales and after-service department.We are usually dedicated to provide customers with high quality and reasonable price product.Most importantly ,we can provide the efficient service.
4. Each procedure will be carefully detected in the technical staff to compelete.accomplish the order in time and delivery on time.
5. During our cooperation,if you have any problem ,you can contact us at anytime,we will do our best to help you.